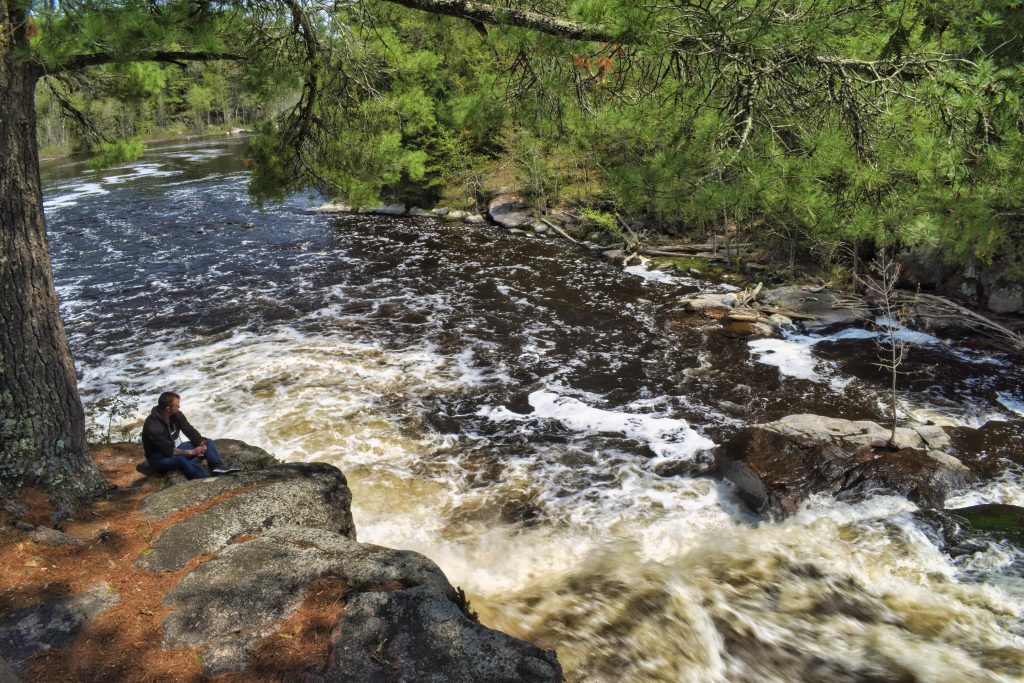
A Wisconsin Idea Seminar participant contemplates the Wolf River at Big Smokey Falls in the Menominee Reservation. Image credit: Marie Zhuikov, Wisconsin Sea Grant
This is the second (and final) story in a series about my weeklong trip around Wisconsin as part of the Wisconsin Idea Seminar. Part 1 described our experience on the University of Wisconsin-Madison campus learning about Ho-Chunk history. Read that story here. This part will describe the rest of the trip in general, focusing on a tour of the Green Bay Packaging Co.

The Historic Indian Agency House in Portage. Image credit: Marie Zhuikov, Wisconsin Sea Grant
Continuing the first day of our tour, a Badger Bus took us to Portage, where we visited the Historic Indian Agency House, which is where the Ho-Chunk people came to collect their government allotments once they were displaced from their lands by settlers. Reading the names of the Native families on the outdoor plaques was a poignant reminder of this traumatic time in history.
Then we traveled to Appleton, where we took a walking tour of the town, learning about
Black history. When the area was first settled, some land and businesses were owned by Black people, but by the 1930s, the town was entirely white due to organized, unofficial harassment that drove Blacks away. That has thankfully turned around so much that there’s even a soul food restaurant in town, which is where we ate supper.
On Day 2, we drove to Green Bay where we toured the impressive Green Bay Packaging Co. There was a rumor floating around on the bus that this was the business that the Green Bay Packers football team was named after. Later, I discovered through my own research that this wasn’t true. The Packers were named after a meat-packing plant, which was one of their first sponsors. See, this Minnesotan really is learning about Wisconsin culture!
Green Bay Packaging makes paper from recycled materials. That paper is then used to make boxes. They don’t make the boxes on-site – they ship their paper elsewhere for that. Two years ago, they expanded their facilities on the same land by the bay. Much of the process is automated. Even so, the company employs more workers than before. In the early 1990s, this mill was one of the first in the world to become totally effluent free (zero discharge of wastewater).
 We were led through the plant by Olivia Durocher, project development specialist, and Andrew Stoub, environmental manager. Durocher said that 50% of their recycled materials comes from “big box” companies like Target and Walmart and the other 50% comes from consumers. They produce about 550 tons of paper per year.
We were led through the plant by Olivia Durocher, project development specialist, and Andrew Stoub, environmental manager. Durocher said that 50% of their recycled materials comes from “big box” companies like Target and Walmart and the other 50% comes from consumers. They produce about 550 tons of paper per year.
“Wisconsin has been a top producer of paper for a long time,” Durocher said. “We’re happy to have a hand in that.”
She explained that a paper fiber can be recycled seven times before it becomes too short to be used any more. That’s why other mills still use trees to make paper. “If you stopped introducing virgin fiber into the system, the entire country would run completely out of boxes in about six months or less. That’s why it’s important to continue to plant trees and use virgin fiber to produce kraft paper. It introduces that virgin fiber into the system. That’s why we can’t have all the mills be recycled mills,” Durocher said.
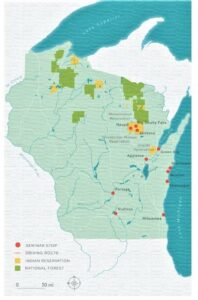
Wisconsin Idea Seminar stops. Image credit: University of Wisconsin-Madison
Stoub said the water used in the plant does not come from the bay. About half of the water is recycled from treated water the mill has already used and half comes from treated wastewater from the city of Green Bay. The company uses the methane gas produced by their wastewater digestor to feed their boilers instead of burning the gas off, which many facilities do. Plus, the gas fuels a generator that produces enough electricity to power the mill’s wastewater treatment plant. “It’s a pretty cool sustainable system,” Stoub said.
During our tour of the plant, most impressive to me was its automated 100,000-square-foot paper warehouse. According to Durocher, it’s the largest vertically stacked paper warehouse in the Western Hemisphere. It holds 8,000 rolls of paper, which is the equivalent of 26,000 tons of paper – about 22 days of inventory. No people are allowed in the warehouse because of the danger of a huge tower of paper falling on them. As you can guess, when they built the floor for the warehouse, they took pains to ensure it was totally level!
We were able to view the warehouse through indoor windows. The paper is moved around by four vacuum cranes (Konecranes), which each employ 14,000 pounds of suction. Compared to mechanical cranes, the vacuum cranes allow workers to store the rolls closer together and move them around faster. Paper from the warehouse is shipped out by rail and trucks. Alas, I don’t have any photos of the warehouse or the inside of the mill because we weren’t allowed to take them.
Stoub said you can tell that a box came from the company’s materials because it will have their logo on it.

The business end of a cow at Soaring Eagle Dairy. Image credit: Marie Zhuikov, Wisconsin Sea Grant
Highlights from the rest of the five-day trip included a visit to the Menominee Reservation where we learned about their sustainable timber harvesting practices and sawmill operation. We also visited Big Smokey Falls on the Wolf River on the reservation, where we had a chance to get a feel for the land and contemplate what we’d learned so far. That day ended with a tea-making workshop led by Menominee Elder Bonnie McKiernan. We made a mixture that’s good for colds, with bee balm (which I have a ton of in my yard; I did not know it was edible), peppermint and mullein.
On Day 4, we visited Soaring Eagle Dairy in Newton, a woman-run business. I learned more than I ever wanted to know about how that industry runs. Their milk is used by Land-O-Lakes Inc.
During the final day, we took a walking tour of Milwaukee’s South Side and visited Escuela Verde, a charter school. The tour ended with an art project where we were able to reflect on our experiences.
Through it all, our bus driver Bob was with us. He literally held our lives in his hands, and we respected him greatly. He became a favorite among us.
I came away from the experience feeling more familiar with Wisconsin. This Minnesotan still has a lot to learn, but I feel a bit more confident in my knowledge base now.


